Modern serverless applications increasingly rely on event-driven architectures, where AWS Lambda functions process events from various sources like Amazon Kinesis, Amazon DynamoDB Streams, Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS), Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK), and self-managed Apache Kafka.
Although event source mappings (ESM) offer a powerful mechanism for integrating AWS Lambda with stream and queue-based sources, configuring them to align with high-level architectural goals can sometimes involve navigating a broad set of options and parameters. Achieving an optimal configuration typically requires mapping developer intent to several technical settings, which can introduce inefficiencies or operational overhead.
In May 2025, AWS launched the AWS Serverless MCP Server, which provided AI-powered assistance for serverless application development, including infrastructure provisioning, deployment automation, and architectural guidance. Building on this foundation, AWS is now expanding the Serverless MCP Server to include specialized ESM tools.
These new dedicated tools in the AWS Serverless Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server combine the power of AI assistance with ESM expertise to enhance how developers build and manage event-driven serverless applications using Lambda. The new ESM tools provide contextual guidance specific to ESM configuration that address the challenges of event-driven development.
This post describes how the new tools under Serverless MCP Server work with AI coding assistants to streamline event source mapping management. Learn how to use this solution to accelerate your event-driven development workflow and build robust, high-performing applications more efficiently.
Overview
An event source mapping is a Lambda resource that reads items from stream and queue-based services and invokes a function with batches of records. Within an event source mapping, resources called event pollers actively poll for new messages and invoke functions. Using ESMs, AWS Lambda functions can automatically consume events from various sources without requiring custom polling infrastructure. Lambda handles the complexity of scaling, batching, filtering, and error handling, helping developers focus on business logic.
Navigating ESM configurations
Configuring these mappings optimally, especially for virtual private cloud (VPC)-based sources like Apache Kafka, requires additional understanding of networking, permissions, and performance tuning.
When working with event source mappings, developers need to address several technical considerations. For Kafka Streams using VPC-based Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka or self-managed Apache Kafka, configurations involve networking setup to enable Lambda access to Kafka topics. Developers must manage bootstrap servers, AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions, and topic access settings, while also handling authentication including SASL/SCRAM credentials, mTLS certificate management, and Kafka ACL permissions.
Developers need to know how to translate performance requirements, such as processing 1,000 events per second, into specific ESM parameter configurations. Depending on the stream source, this involves determining appropriate batch sizes, parallelization factors, and retry policies while managing iterator age, offset lag and potential timeout issues. Additionally, developers need visibility into configuration effectiveness and other diagnostic information to optimize resource allocation and ensure reliable event processing.
Dedicated event source mapping tools
The new ESM tools in the open source AWS Serverless MCP Server address these challenges by providing AI assistants with proven knowledge of event source mapping patterns and best practices. These tools guide developers through the entire ESM lifecycle, from initial setup to optimization and troubleshooting. They also enhance the event-driven development experience by translating the developers intent into detailed, technical configuration, helping developers express high-level goals such as desired throughput, latency, or reliability requirements. The new tools cover all areas of event source mapping management:
- Setup and configuration: Developers initialize new event source mapping configurations using AWS Serverless Application Model (AWS SAM) templates, select appropriate event source settings, and configure networking requirements for VPC-based sources like Amazon MSK.
- Optimization and tuning: As applications evolve, the tools assists with fine-tuning ESM parameters like batch size, batching window, retry policies, and parallelization factors based on performance goals and telemetry data.
- Troubleshooting and diagnostics: Specialized tools diagnose ESM connectivity issues, analyze Amazon CloudWatch Logs and metrics, and recommend solutions for common problems like VPC misconfigurations or permission errors.
Event source mapping tools in action
This example walks you through a scenario of creating, optimizing, and troubleshooting an event source mapping for Amazon MSK to demonstrate the capabilities of the new ESM tools.
Prerequisites and installation
To get started, download or update the AWS Serverless MCP Server from GitHub or Python Package Index (PyPi) and follow the installation instructions. You can use this MCP server with any AI coding assistant of your choice, such as Amazon Q Developer, Cursor, Cline, Kiro, and more.
Add the following code to your MCP client configuration:
The Serverless MCP Server incorporates built-in guardrails to ensure secure and controlled development. By default, the server operates in a read-only mode, allowing only non-mutating actions. With this safety-first approach, you can explore ESM capabilities and architectural patterns while preventing unintended changes to your applications or infrastructure.
Creating and configuring an event source mapping
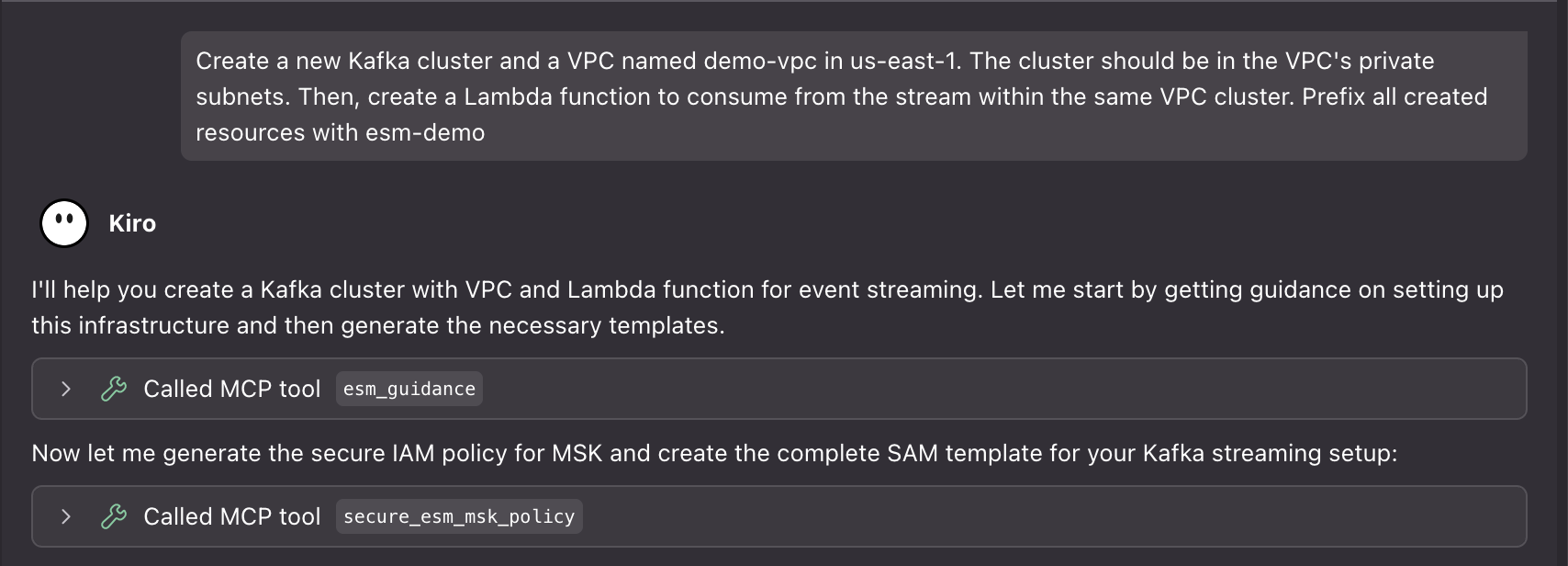
Imagine you want to set up a Lambda function to process events from an Amazon MSK cluster. Start by prompting your AI assistant:
Create a new Kafka cluster and a VPC named <your-vpc-name> in <your-aws-region>. The cluster should be in the VPC’s private subnets. Then, create a Lambda function to consume from the stream within the same VPC cluster. Prefix all created resources with <your-prefix>.
The agent uses the esm_guidance to receive tailored guidance based on your use case and performance requirements. The tool analyzes your intent and provides step-by-step instructions for setting up the ESM with optimal configurations.
Apart from creating deployment and initialization scripts and supporting documentation, properly configured IAM polices and security groups rules to access the cluster are also generated. The assistant then validates the ESM parameters against AWS limits and best practices.
Next, you want to understand the networking requirements:
My Kafka cluster is in a VPC. What networking configuration do I need for Lambda to access it?
The Serverless MCP Server provides specialized guidance for VPC-based Kafka configurations using the esm_guidance tool with guidance_type=”networking”. This guidance provides detailed information about subnet requirements, security group rules, and NAT gateway setup, and it validates your network topology for reliable connectivity.
Optimizing event source mapping performance
After your ESM is running, you notice that processing latency is higher than expected. You can ask for optimization guidance:
I have an ESM with UUID <your-esm-uuid> in <your-aws-region>. My target throughput is between 10 MB/s and 100 MB/s. Please update my ESM configuration to meet these throughput requirements while optimizing the cost of the event pollers.

The server uses the esm_optimize tool to analyze your current configuration and provide optimization recommendations. The tool supports three main actions:
- Analysis mode: (action=
"analyze") Analyzes configuration tradeoffs for your optimization targets (throughput, latency, cost, failure rate) - Validation mode: (action=
"validate") Validates your ESM configuration against AWS limits and event source restrictions - Template generation: (action=
"generate_template") Creates updated AWS SAM templates with optimized configurations
You can use this tool to get guidance on your event source mapping configurations for Amazon SQS, Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, and Amazon DynamoDB Streams. Here are two examples:
I have a Kinesis stream with 100 shards receiving 100 MB/s of data. My Lambda function processes each record in about 50ms. Currently, my ESM has ParallelizationFactor=1 and BatchSize=100, but I’m seeing high iterator age (over 60 seconds) during peak times. How should I optimize my ESM configuration to reduce processing latency and handle the throughput?
I have an SQS standard queue that receives 50,000 messages per hour during peak times. Each message takes about 2 seconds to process. My current ESM configuration has BatchSize=10 and no ScalingConfig set. I’m seeing message delays during peak hours. How should I optimize my ESM configuration for better throughput while keeping costs reasonable?
The tool generates updated AWS Serverless Application Model (AWS SAM) templates with the recommended configurations, making it easy to apply the changes through your deployment pipeline. However, it always requires explicit user confirmation before any deployment.
Troubleshooting event source mapping issues
When an issue arises, the ESM tools provide diagnostic capabilities. For example, if your ESM stops processing events:
I have a cluster called <your-kafka-cluster-name> and a consumer Lambda function named <your-lambda-function-name>in <your-aws-region>. Please investigate why my ESM (UUID: <your-esm-uuid>) trigger is not working and provide updated configurations to resolve the issue.
The server uses the esm_kafka_troubleshoot tool to provide comprehensive troubleshooting for Apache Kafka clusters. The tool supports two main modes:
- Diagnostic mode: (issue_type=
"diagnosis") Analyzes your ESM status and provides diagnostic indicators. This helps identify whether timeouts occur before or after reaching Kafka brokers. It categorizes issues into specific types for targeted resolution. - Resolution mode: Provides step-by-step resolution guidance for specific issues.
The tool automatically detects your event source type and provides tailored guidance. It validates VPC connectivity, examines IAM permissions, checks security group configurations, and analyzes CloudWatch Logs to provide a detailed diagnosis report with specific remediation steps.
Key benefits
The event source mapping tools in the AWS Serverless MCP Server provide unique advantages over traditional event source mapping configuration approaches:
- AI-powered configuration translation: The tools translate high-level developer intent (such as process 1,000 events per second) into specific ESM parameters like batch size, parallelization factor, and batching window.
- Complete infrastructure-as-code generation: Unlike generic AWS CLI tools that provide individual commands, ESM tools generate complete AWS SAM templates, initialization scripts, cleanup scripts, and validation scripts for end-to-end automation.
- Proactive network validation: For VPC-based event sources like Amazon MSK or self-managed Kafka, the tools validate network topology, security group rules, and connectivity before deployment, preventing common silent failures.
- Context-aware troubleshooting: The diagnostic tools correlate ESM status, CloudWatch metrics, VPC configuration, and IAM permissions to provide comprehensive root cause analysis with specific remediation steps.
New tools available in the Serverless MCP Server
The event source mapping tools are designed to minimize trust permission prompts by using a small set of primary tools that internally call specialized functions. The tools can be classified into three main categories:
esm_guidance: This tool provides comprehensive guidance on creating and configuring event source mappings for all event sources (DynamoDB, Kinesis, Kafka, SQS). It handles setup, networking guidance, and troubleshooting based on the guidance_type parameter. The tool automatically generates AWS SAM templates, IAM policies, and security group configurations.esm_optimize: This advanced optimization tool analyzes configuration tradeoffs, validates ESM settings, and generates AWS SAM templates for performance tuning. It supports three actions:- analyze: Provides configuration tradeoff analysis for failure rate, latency, throughput, and cost optimization
- validate: Validates ESM configurations against AWS limits and event source restrictions
- generate_template: Creates AWS SAM templates with optimized configurations
esm_kafka_troubleshoot: This specialized troubleshooting tool for Kafka ESM issues supports both Amazon MSK and self-managed Apache Kafka clusters. It also provides diagnostic capabilities and step-by-step resolution guidance for connectivity, authentication, and network issues.
The primary tools internally call specialized helper functions to provide comprehensive functionality that help generate IAM polices, security groups, scaling and concurrency configurations, and validate configurations.
Visit the Serverless MCP Server documentation for the full list of tools and resources.
Best practices and considerations
When building event-driven applications with the AWS Serverless MCP Server, start by using its guidance tools for architectural decisions. The server helps you choose appropriate event sources, understand networking requirements, and configure optimal settings based on your performance goals.For Kafka-based ESMs, pay special attention to VPC configuration. Use the server’s network troubleshooting tools to validate connectivity before deployment. The server can detect common issues like missing NAT gateways, incorrect security group rules, or subnet routing problems.Monitor your event source mappings continuously using the server’s diagnostic tools. Set up alerts for key metrics like iterator age, error rates, and throttling. The server can help you interpret these metrics and recommend configuration adjustments to maintain optimal performance.
Conclusion
The new event source mapping tools in the open-source AWS Serverless MCP Server simplify event source mapping management throughout the development lifecycle, from initial setup to ongoing optimization and troubleshooting. By combining AI assistance with ESM expertise, it helps developers build and deploy event-driven applications more efficiently while avoiding common configuration pitfalls.
As organizations continue to adopt event-driven serverless computing, tools that simplify ESM management and accelerate delivery become increasingly valuable.
To get started, visit the GitHub repository and explore the documentation. Share your experiences and suggestions through the GitHub repository to improve the MCP server’s capabilities and help shape the future of AI-assisted event-driven development.
For more serverless learning resources, visit Serverless Land.