This blog post discusses the AWS Lambda as orchestrator anti-pattern and how to redesign serverless solutions using AWS Step Functions with native integrations.
Step Functions is a serverless workflow service that you can use to build distributed applications, automate processes, orchestrate microservices, and create data and machine learning (ML) pipelines. Step Functions provides native integrations with over 200 AWS services in addition to external third-party APIs. You can use these integrations to deploy production-ready solutions with less effort, reducing code complexity, improving long-term maintainability, and minimizing technical debt when operating at scale.
The Lambda as orchestrator anti-pattern
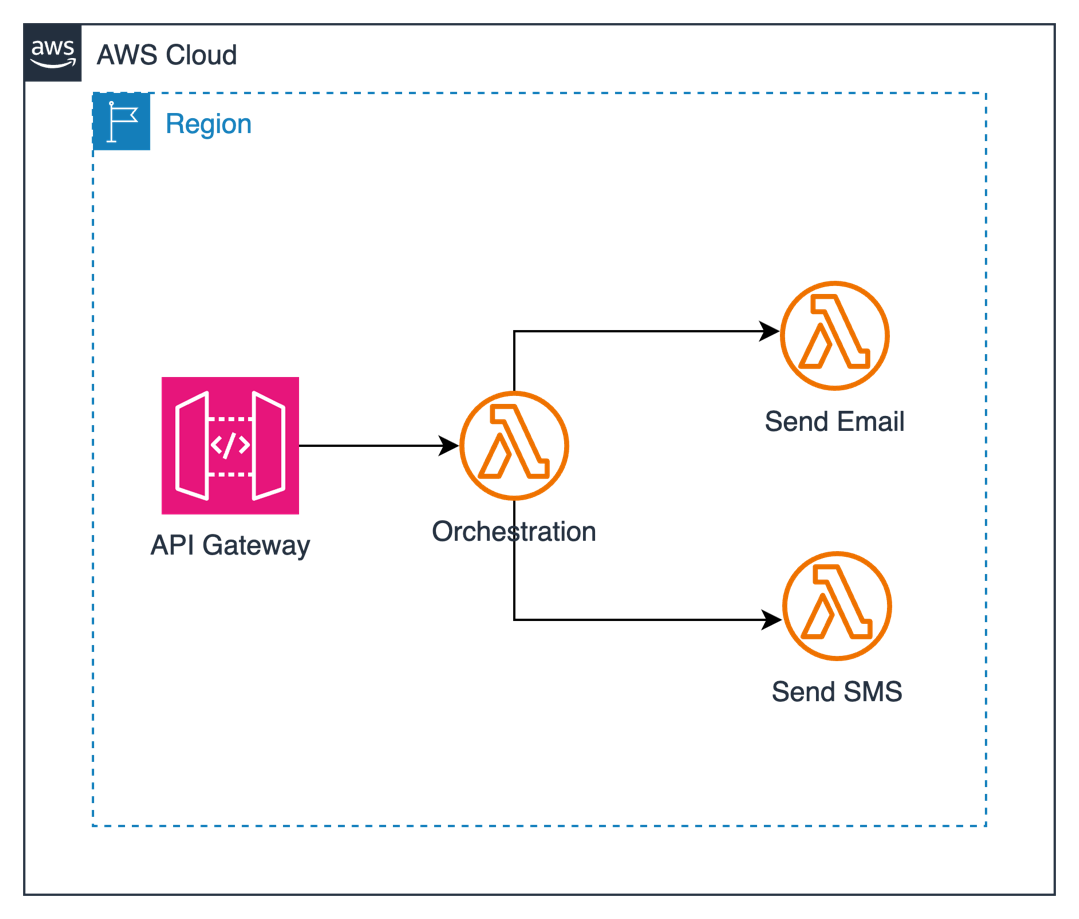
Let’s examine a common anti-pattern: using a Lambda function as an orchestrator for message distribution across multiple channels. Consider this real-world scenario where a system needs to send notifications through SMS or email channels based on user preferences, as shown in the following diagram.
The payload examples for this scenario are:
- Send SMS only:
- Send email only:
- Send both SMS and email:
Here’s how it typically starts—with a Lambda function acting as an orchestrator:
This approach has the following problems:
- Complex error handling: The orchestrator needs to manage errors from multiple function invocations.
- Tight coupling: Functions are directly dependent on each other.
- Limited execution time: The orchestrator Lambda function continues running while sub Lambda functions execute. This could lead to the orchestrator Lambda function timing out.
- Idle resources: Because the orchestrator Lambda function is sitting idle waiting for returns from other Lambda functions, in this case, the user is now paying for idle resources.
Rearchitecting with Step Functions
You can rebuild the logic using Step Functions and Amazon States Language to replace the Lambda orchestrator function. You can use the Choice state in Amazon States Language to define logical conditions to follow a specific path. This approach reduces code maintenance complexity because you define the conditions using Amazon States Language. You can also use it to to extend the functionality with minimal changes to the codebase.
The following Step Functions workflow diagram shows the rearchitected version of the previous Orchestrator Lambda function:
The following Amazon State Language represents the workflow:
This Step Functions implementation offers several advantages:
- Native service integration: Direct integration with Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS), Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES), Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon CloudWatch eliminates the need for wrapper Lambda functions
- Visual workflow: The execution flow is visible and maintainable through the AWS Management Console
- Built-in error handling: Retry policies and error states can be defined declaratively
- Parallel execution: The
Parallelstate handles multiple channel delivery efficiently - Simplified logic: The
Choicestate replaces complexif-elsestatements - Centralized data flow: Input and output are managed consistently across states
- Enhanced workflow duration capabilities: Step Functions Standard workflows support executions that run for up to one year, compared to the 15-minute maximum execution time for Lambda functions
Comparing Lambda function as orchestrator to Step Functions
The summary of different features implemented on Lambda function as orchestrator and Step Functions is reflected in the following table:
| Feature | Lambda function as orchestrator | Step Functions |
| Orchestration logic | Implemented in Python with nested if-else statements. | Defined declaratively using the Choice state |
| Multi-channel delivery | Sequential function invocations. Parallel execution using function’s logic. | Parallel execution using the Parallel state |
| Service integration | Requires SDK calls or separate Lambda functions. | Direct integration with AWS services (Amazon SNS, DynamoDB) |
| Error handling | Custom try-except blocks in Python. | Built-in error states and retry policies |
| Data persistance | Custom code to interact with DynamoDB. | Native DynamoDB integration with putItem task |
| Metrics logging | Custom code to call CloudWatch. | CloudWatch Metrics SDK integration |
Implementation considerations
Review the following considerations when re-architecting a Lambda function orchestrator to Step Functions:
- State machine type: Choose between Standard (up to 1 year runtime) and Express (up to 5 minutes) workflows based on your needs.
- Input/output management: Parameters manipulation reduces the development effort and give flexible alternatives to implement the workflow:
- Parameters: Selects specific input fields to pass to the next state
- ResultSelector: Filters the state response to include only relevant fields
- ResultPath: Stores the processed result in a specific path of the state input
- OutputPath: Determines what data passes to the next state
A code snippet for these features is:
- Error handling: Implement retry policies and catch errors at both the task and state machine levels.
- Monitoring: Set up CloudWatch logs and metrics for your state machine to track executions and performance.
Benefits of using Step Functions
Using Step Functions for rearchitecting scenarios bring the following benefits:
- Reduced code complexity: The business logic is now defined in Amazon States Language rather than distributed across multiple Lambda functions.
- Improved maintainability: Developers can make workflow changes by modifying the Amazon States Language, often modifying several Lambda functions.
- Native AWS service integrations: Step Functions offers direct integrations with over 200 AWS services, which you can use to connect and coordinate AWS resources without writing custom integration code.
- Cost optimization: By using direct service integrations, there are fewer Lambda invocations and reduced costs.
- Long-running processes: Step Functions can manage workflows that run for up to a year, beyond the 15-minute limit for Lambda functions.
Conclusion
Rearchitecting Lambda-based applications with Step Functions can significantly improve maintainability, scalability, and operational efficiency. By moving orchestration logic into Step Functions and using its native service integrations, you can create more robust and manageable serverless applications.
While this post focused on a message distribution workflow, the principles apply to many serverless architectures. As you develop your applications, consider how Step Functions can help you build more resilient and scalable solutions.
To learn more about serverless architectures visit Serverless Land.